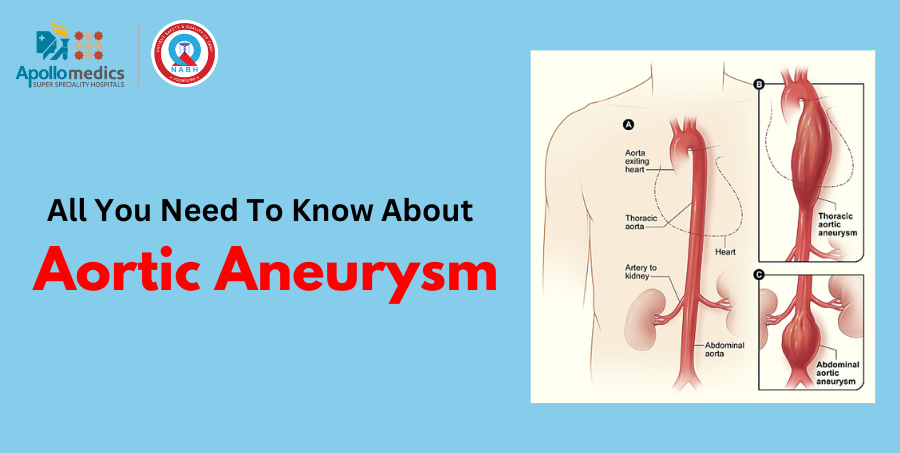
The aorta is the body’s largest artery, running from the heart through the chest and abdomen. Aortic diseases primarily affect the elderly and become more common as they age. They account for significant cardiovascular morbidity and mortality worldwide.
Aortic aneurysm is a disease that causes a balloon-like dilatation of the aorta [main blood vessel supplying blood to the entire body], which continues to grow over time.
Aortic aneurysm and dissection are both serious medical conditions. Aortic aneurysm rupture is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, with 50% of patients dying before reaching the hospital.
Types of Aortic Aneurysm
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm [AAA]- Involving the part of the aorta in the abdominal cavity
Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm (TAA]- Involving the part of the aorta in the chest
Thoraco-Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (TAAA]- Involving parts of aorta in the chest as well as the abdomen
Who Are At A Risk Of Having Aortic Aneurysm?
Risk Elements
- Old age (over 60 years)
- Tobacco use—whether smoking or chewing [Any age group]
- Type 2 diabetes
- Blood pressure that is too high
- Obesity, high blood and cholesterol levels
What Are the Symptoms of an Aortic Aneurysm?
- Abdominal pain that comes on suddenly and is severe
- Excruciating Back pain
- Swelling/heaviness in the stomach Reduced hunger sensation/appetite
How Is the Diagnosis Made?
- The diagnosis may be confused with renal stone, gastritis, hernia or lumbar spine disease.
- Abdominal ultrasonography/CT scans and some tests are required (as advised by the vascular surgeon)
- Consult a qualified vascular-endovascular surgeon immediately at Apollomedics hospitals, Lucknow
Treatment Options
Medical treatment
Patients with an aneurysm smaller than 5.5 cm in men and smaller than 5 cm in women are usually treated with medications and a 6-monthly serial evaluation with a CT scan. If the aneurysm is seen to be growing in size, the patient is advised to seek treatment.
Who requires immediate assistance?
- Aneurysms that are larger than 5.5 cm in men and 5 cm in women.
- Serial CT scans show an expanding aneurysm.
- Aneurysm ruptured/impeding rupture
Advanced treatment Options
Endovascular Aortic Repair (EVAR/TEVAR):
It is now the standard of care. The procedure is carried out in a Vascular Cath lab. It entails inserting an endovascular stent graft into the aorta through small incisions at the top of the leg. This graft covers the abnormal aorta and prevents blood from flowing into the aneurysm. As a result, the aneurysm closes down and shrinks over time.
Open surgical Repair
In patients who are not candidates for endovascular repair, this procedure is used. The dilated portion of the aorta is exposed via an incision in the abdomen or abdomen and chest, followed by the insertion of a synthetic graft [tube] to replace the diseased aorta. The graft is hand-sewed to the non-diseased portions of the aorta before the aneurysmal sac is closed around it.
A hybrid strategy
This approach is used to treat complex aortic aneurysms.
The Bottom line
Endovascular aortic repair is becoming the norm for both simple and complex aneurysms.
As soon as there is a suspicion of an aortic aneurysm, seek the advice of a vascular expert at Apollo hospitals Lucknow. Diagnostic evaluation of aortic disorders has significantly improved in India over the last decade, allowing for earlier diagnosis and therapeutic intervention.
Written by